Jim Krause | Classes | C228 Multi-Cam TV Studio Production 1
Week 14
Announcements/Reality Check
- Cover remaining assignments:
- Remote Multi-Camera assignment (due date extended to 12 PM Monday, April 26, 2021)
- The Spring 2021 C228 Final Exam (scheduled by the Registrar) is Monday, May 3 from 10:10 AM - 12:10 PM. It will be administered through Canvas. It will be available earlier in the morning but MUST be completed by 12:10 PM. (Expect it to take about 45 minutes.)
Readings:
- These on-line lecture notes
Agenda:
- Review Remote Productions, Site surveys & Distribution
- Cover new trends in production
Remote Productions (Review)
Remote productions can be classified into three broad categories:
- ENG - Electornic News Gathering
- EFP - Electronic Field Production (single or multi-camera)
- Big Remotes - Large, multi-camera productions
Electronic News Gathering
News happens in an instant. There is no time for site surveys and production people must move quickly to cover developing events.
Electronic Field Production
Electronic FIeld Production is anything that happens outside of the controlled studio environment. There is time to scout locations, carry out site surveys, and complete thorough preproduction. FIeld production can be in the form of single or two camera shoots, or even a multi-camera package.
Big Remotes
A big remote is a large multi-camera production used to cover a major scheduled event. This could be the Oscars, the Tony Awards, the Olympics, or a Big Ten football game. In sports remotes, crews can be very large - more than 100 people are needed for a major sports event.
Site surveys are required for Electronic Field Production and for Big Remotes. Typically the Director and/or chief technical personnel schedule a site visit well ahead of the scheduled production. They work with the site's facilities coordinator to determine:
- Sources of power
- Parking & access
- Pemrits
- Bathrooms
- Communication
- Uplink/downlink location
- Physical space (dimensions, ceiling height, windows, etc.)
- Potential sound problems
- Lighting and other visual issues
- Camera positions
- Length of cable runs
- Security
One should being a camera, sketchpad, compass, and tape measure to a site survey and make a rough sketch of the layout. One needs to be able to make an accurate floor plan from the information they bring back. Put a compass rose on your sketch. A good location sketch aid the director in a number of ways: deciding camera positions, focal lengths of lenses, lighting, audio & communication systems and cable runs.
The Remote Multi-Camera Proposal and Budget assignment is your chance to carry out a site survey and plan a remote production.
Signal transport & delivery -----------------------------------------
Programming can be delivered to subscribers in four ways:
- Terrestrial broadcast
- Satellite (Direct TV, DISH, etc.)
- Cable/Wired (ATT, Comcast, etc.)
- Mobile (Cell phone networks such as Verizon, ATT, Sprint, etc.)
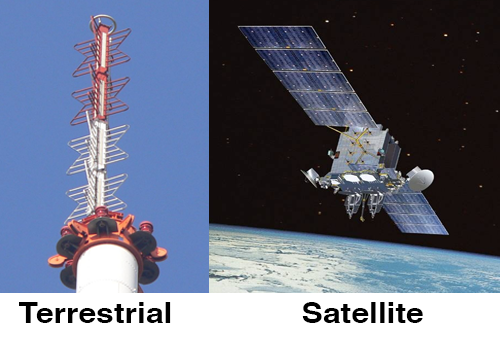

Terrestrial TV stations broadcast radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Use of the electromagnetic spectrum is overseen by the FCC (Federal Communications Commission). It's used by television, radio, the military, cell phone companies, and even your garage door openers.
Digital Television (DTV) - Analog broadcast ended February 19, 2009. The ATSC (Advanced Televesion Systems Committee) is the organization that developed and guides DTV broadcast standards.
ATSC - A number of industry associations, corporations, and educational institutions formed the Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) in 1982. The ATSC is a not-for-profit organization that develops voluntary standards for advanced television systems (www.atsc.org). Such advanced systems include enhanced analog TV, digital TV (DTV), standard definition TV, high-definition TV, and data services. The ATSC’s published broadcast standards are voluntary unless adopted and mandated by the FCC.
Satellite - All geosynchronous communication satellites orbit the earth above the equator 22,236 miles / 35,786 km above the earth). All of the downlink satellite dishes you see are pointed towards the south (somewhere over the equator).
Satellites used for broadcast are either C or KU band. KU band dishes can be smaller (2 feet). Direct broadcast satellites or DBS (such as DISH or DirectTV) operate on the KU band.
- Uplinks (send to satellite)
- Downlink (receive)
Microwave transmission - Power & size varies. Very small, focused signal. Don’t stand in front of one! Can go from camera to truck, truck to relay station, truck to satellite, or directly to the station.
Cable/Wired-based - Twisted pair, Coaxial & fiber-optic.
Compared to cable or fiber-optic, twisted pair (E.g. traditional phone line) is capable of carrying the least amount of information. Most cable companies started out with coaxial cable. Most now are using fiber-optic, which is capable of carrying more information.
Mobile/Cell Distribution - The widespread use of portable devices has prompted providers to offer content for mobile customers. Television distributed over cell phone networks and viewed on portable devices.
Convergence - These have been interesting times, as cable companies are now offering phone service and phone companies are offering TV.
Many consumers are giving up monthly cable/satellite packages, tuning in to TV programming via the Internet. It's possible to get a great deal of free programming, which is usually interspersed with commercials. (Sound familiar?)
Three World TV Standards
- NTSC (National Television Systems Committee) definition of standard definition TV, (used in North America, some of South America, Japan, etc) uses a frame rate close to 30, roughly 29.97 frames per second. There are 525 scan lines; approximately 480 of these are visible. The HD (high definition) standard for broadcast has been created by the ATSC, the Advanced Television Systems Committee, which was formed at the urging of the FCC to establish standards for the new high definition formats.
- PAL (Phase Alternate Line) is used in most of Europe, Australia, & Asia and runs at 25 frames per second using 625 lines.
- SECAM (Sequential Color and Memory)
New Trends in Multi-Camera Studio Production -----------------------------
More and more TV studios are using motion control cameras, flourescent and LED lighting, and virtual sets.
Multi-camera field production is incorporating camera mounts which allow for more interesting angles and dynamic shots.
Motion Control & Robotic Cameras:
Shows that have elaborate openings are often programmed with elements such as robotic camera support. This provides a way to use repeatable and complex moves easily.
Vinten's robotic-controlled pedestal:

- Vinten Radamac Control System overview
- Many such as Ross's Furio work on tracks and are suitable for live performance production
- Bot & Dolly's Iris System (robotic camera used on Gravity)
- MrMoco Bolt - Behind the Scenes
- Here's a behind the scenes look at how one person can control multiple cameras.
- These things don't always work as expected.
Virtual Sets
- http://vimeo.com/63709035 (Vizrt 2013 demo - pretty impressive)
SkyCam - cable-mounted camera system
2K, 4K, UltraHD, and beyond.....
HD is great but there's something even better: 2K and 4K. Check out the wikipedia entry on it.
2K provides only slightly more information than HD. 2048 pixels per line compared with 1920. But the format was embraced by the digital cinema industry. The Phantom Menace introduced the world to Digital Cinema. Digital Cinema is not about production- but the distribution of theatrical content.
Most have ignored 2K and focused on 4K, which essentially provides 4 times the information as HD.
Just as HD comes in varying pixel dimensions for broadcast and recording 4K comes in different sizes as well. Most variations of 4K have 4096 pixels per line.
UltraHD (Ultra High-Definition) refers to any format from 4K to above.
It's possible to produce and deliver content at even much higher resolutions. (E.g. 10k 10328 x 7760 pixels). Here's a link to a 10k timelapse video shot in Brazil.
Metadata & Closed Captioning
Metadata is embedded information about the program itself (such as the title, running time, production notes, etc). It can include, but is not limited to:
- timecode
- camera
- closed captions
- exposure
- gain
- clip name
- running time / duration
- latitude/longitude
- audio levels
- DRM (digital rights management)
Terms & abbreviations you should know:
- 2K
- 4K
- ATSC
- Big Remote
- Closed-captioning
- Digital Cinema
- Downlink
- ENG
- EFP
- Metadata
- NTSC | PAL | SECAM
- Robotic Pedestal
- Site Survey
- SkyCam
- Ultra HD
- Uplink
- Virtual Set


