Jim Krause | Classes | C228 Multi-Cam TV Studio Production 1
Week 13
Announcements/Reality Check
- Quiz #5 This week in lab. (legal issues and remote productions)
- Produce Performance Projects this week
- Cover remaining assignments:
- Critiques for Dramatic/Comedic Scenes due this week.
- Critiques for Performance Projects are due next week.
- Pre-production packets for Final Projects due by 5 PM this Friday. This is a group grade.
- Remote Multi-Camera assignment due by 5 PM next Friday, (April 23)
- The Spring 2021 C228 Final Exam (scheduled by the Registrar) is Monday, May 3 from 10:10 AM - 12:10 PM. It will be administered through Canvas. It will be available earlier in the morning but MUST be completed by 12:10 PM. (Expect it to take about 45 minutes.)
Agenda:
- Review IP
- Remote Productions
- Site surveys
- DTV Signal / Distribution
- Review the Remote Multi-Camera assignment.
Remote Productions
Remote productions can be classified into three broad categories:
- ENG - Electornic News Gathering
- EFP - Electronic Field Production (single or multi-camera)
- Big Remotes - Large, multi-camera productions
Electronic News Gathering
News happens in an instant. There is no time for site surveys and production people must move quickly to cover developing events.
Electronic Field Production
Electronic FIeld Production is anything that happens outside of the controlled studio environment. There is time to scout locations, carry out site surveys, and complete thorough preproduction. FIeld production can be in the form of single or two camera shoots, or even a multi-camera package.
Big Remotes
A big remote is a large multi-camera production used to cover a major scheduled event. This could be the Oscars, the Tony Awards, the Olympics, or a Big Ten football game. In sports remotes, crews can be very large - more than 100 people are needed for a major sports event.
Site surveys are required for Electronic Field Production and for Big Remotes. Typically the Director and/or chief technical personnel schedule a site visit well ahead of the scheduled production. They work with the site's facilities coordinator to determine:
- Sources of power
- Parking & access
- Pemrits
- Bathrooms
- Communication
- Uplink/downlink location
- Physical space (dimensions, ceiling height, windows, etc.)
- Potential sound problems
- Lighting and other visual issues
- Camera positions
- Length of cable runs
- Security
One should being a camera, sketchpad, compass, and tape measure to a site survey and make a rough sketch of the layout. One needs to be able to make an accurate floor plan from the information they bring back. Put a compass rose on your sketch. A good location sketch aid the director in a number of ways: deciding camera positions, focal lengths of lenses, lighting, audio & communication systems and cable runs.
Jim's KSB site survey excerpts:
------------------------- Info below will NOT be in Quiz #5 -----------------
Signal transport & delivery
Programming can be delivered to subscribers in four ways:
- Terrestrial broadcast
- Satellite (Direct TV, DISH, etc.)
- Cable/Wired (ATT, Comcast, etc.)
- Mobile (Cell phone networks such as Verizon, ATT, Sprint, etc.)
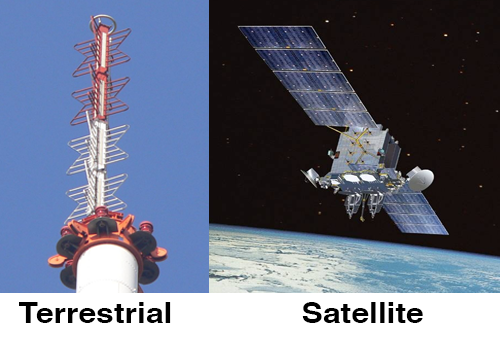

Terrestrial TV stations broadcast radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Use of the electromagnetic spectrum is overseen by the FCC (Federal Communications Commission). It's used by television, radio, the military, cell phone companies, and even your garage door openers.
Digital Television (DTV) - Analog broadcast ended February 19, 2009. The ATSC (Advanced Televesion Systems Committee) is the organization that developed and guides DTV broadcast standards.
ATSC - A number of industry associations, corporations, and educational institutions formed the Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) in 1982. The ATSC is a not-for-profit organization that develops voluntary standards for advanced television systems (www.atsc.org). Such advanced systems include enhanced analog TV, digital TV (DTV), standard definition TV, high-definition TV, and data services. The ATSC’s published broadcast standards are voluntary unless adopted and mandated by the FCC.
DTV Formats:
- 1080 i and p (24, 30 & 60 fps. 16 x 9) 1920 x 1080
- 720 i and p (24, 30 & 60 fps. 16 x 9) 1280 x 720
- 480 i and p (24, 30 & 60 fps. Both 16 x 9 and 4 x 3)
(i = interlaced, p = progressive)
Satellite - All geosynchronous communication satellites orbit the earth above the equator 22,236 miles / 35,786 km above the earth). All of the downlink satellite dishes you see are pointed towards the south (somewhere over the equator).
Satellites used for broadcast are either C or KU band. KU band dishes can be smaller (2 feet). Direct broadcast satellites or DBS (such as DISH or DirectTV) operate on the KU band.
- Uplinks (send to satellite)
- Downlink (receive)
Microwave transmission - Power & size varies. Very small, focused signal. Don’t stand in front of one! Can go from camera to truck, truck to relay station, truck to satellite, or directly to the station.
Cable/Wired-based - Twisted pair, Coaxial & fiber-optic.
Compared to cable or fiber-optic, twisted pair (E.g. traditional phone line) is capable of carrying the least amount of information. Most cable companies started out with coaxial cable. Most now are using fiber-optic, which is capable of carrying more information.
- Headend - origination point/control center of the cable system.
- Trunk-line- primary distribution (fiber-optic or coaxial)
- Feeder lines- secondary distribution (through blocks/neighborhoods, etc)
- Drop lines- cables to homes or businesses
- Multicast - delivery of information to a multiple destinations simultaneously
- VOD - Video On Demand
- SDV - Switched Digital Video - A method of broadcasting only channels that are currently tuned, rather than every channel offered at once.
Mobile/Cell Distribution - The widespread use of portable devices has prompted providers to offer content for mobile customers. Television distributed over cell phone networks and viewed on portable devices.
Convergence - These have been interesting times, as cable companies are now offering phone service and phone companies are offering TV.
Many consumers are giving up monthly cable/satellite packages, tuning in to TV programming via the Internet. It's possible to get a great deal of free programming, which is usually interspersed with commercials. (Sound familiar?)
World TV Standards
NTSC (National Television Systems Committee) definition of standard definition TV, (used in North America, some of South America, Japan, etc) uses a frame rate close to 30, roughly 29.97 frames per second. There are 525 scan lines; approximately 480 of these are visible. The HD (high definition) standard for broadcast has been created by the ATSC, the Advanced Television Systems Committee, which was formed at the urging of the FCC to establish standards for the new high definition formats.
PAL (Phase Alternate Line) is used in most of Europe, Australia, & Asia and runs at 25 frames per second using 625 lines.
SECAM (Sequential Color and Memory)
Terms & abbreviations you should know:
- ATSC
- Big Remote
- Downlink
- ENG
- EFP
- NTSC
- PAL
- SECAM
- Site Survey
- Uplink
Lab --------------------------------------------------------------
Learning Objectives:
- Give students practice producing their own performance projects
- Have fun in the process!
Agenda:
- Attendance
- Quiz #5
- Talk about what's due
- Produce performance projects
- Wrap


